Keeping the patient in a specific position ensures the success of a procedure while improving imaging and minimizing pain. In addition, it helps maintain the patient's neutral body alignment by preventing lateral motion and hyperextension, thereby preventing the risk of injury and immobility. Some common posture has become standard practice throughout the medical field and may be used across procedures.
The health care provider and nurses recommend positions to patients so that they are positioned to communicate well while keeping them safe and comfortable. Here we will talk about different body positions to better understand what they are used for and what they look like.
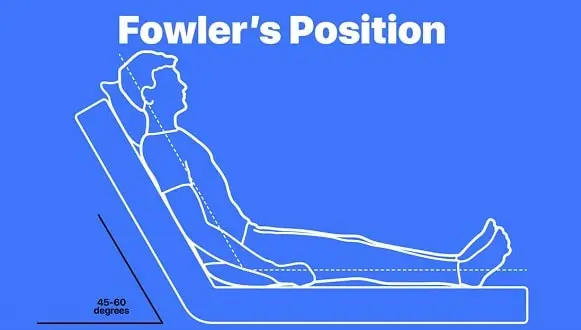
Sometimes called the semi-sitting position, in this position, the patient's head is elevated 45–60 degrees in a semi-recumbent position. The different types of Fowler's positions are the Semi Fowler's 30-45 degree position, the Low Fowler's 15-30 degree position, and the High Fowler's about vertical.
Application & Usage: This position is best suited for patients with neurological, respiratory, or cardiac issues and is often best for patients with a nasogastric tube. As this position pulls the diaphragm to increase the expansion of the lung or chest, it is used for patients with difficulty breathing.
To promote the growth of neck flexion contractures, a pillow should be placed back side of the patient's head. Fowler's position is also suggested for walking or dangling patients. It is ideal for people undergoing surgery that involves neurosurgery or the shoulder. In this position, placing a footboard is indicated so that the feet of the patient is proper alignment.
In the dorsal recumbent or supine position, the patient lies flat on the back with the head while their shoulders are somewhat elevated with the help of pillows unless contraindicated. The position is mainly used for patients having spinal surgery or spinal anaesthesia. Variations on the supine position include bending the legs or extending the arms up and down. In general, it provides comfort for the recuperation of patients after any surgery.
Application & Usage: The patient is supine for a physical assessment and general examination. To keep the patient in this position, a small pillow should be placed under the head to bend the waist.
Additionally, it is essential to have a padded footboard to prevent injury from extended strains and sprains. Despite its benefits, the supine position can increase the risk of nerve and ulcer damage.
In this nursing position, the patient's hips are not flexed while the whole body lies on the stomach, with the head turned to one side. Simply put, the patient's body is made to lie straight with the chest down and back upwards. The ventral side is down, and the dorsal side is up, about 180 degrees opposite.
Application & Usage: The prone position is where the patient's knee and hip joints are allowed full extension. Also, it helps prevent flexion contraction of the knees and hips. The position is best for people who are recovering from surgery on the throat or mouth or who are sedated.
To keep the client in this position, a pillow should be placed under the head as well as a towel or small pillow under the abdomen. The patient lying in the prone state will get support by doing this. People undergoing surgery, such as spine or neck surgery, usually lie in this position.
The orthopaedic position, better known as the tripod position, is an anatomical position commonly used for patients experiencing respiratory problems, including lung disease or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
It is also used for people who are out of oxygen. In this position, the patient stands or sits, leaning forward and supporting the upper part of the body with the hands on the knees while the other body remains on the surface.
Simply put, the patient is sitting on the edge of a bed with a reclined table in front and various pillows on the table for rest. If the patient is in the tripod position, this is an indicator to the medical professional that the patient may be in respiratory distress.
Application & Usage: The orthopaedic or tripod position is useful for patients with exhalation problems. This may be because they may be pressing the lower part of the chest against the edge of the overbed table. In the tripod position, patients with dyspnea are positioned in such a way as to enable maximum chest expansion.
Also called semi-prone, the position is used to place the patient's lower arm behind the back while the upper arm is flexed at the elbow and shoulder.
Application & Usage: Sims' position has been introduced for clients who are paralyzed. The position helps reduce pressure over the sacrum. In fact, pregnant women may stay in this position for comfortable sleeping.
In the Trendelenburg position, the head of the bed is at the bottom, while the foot of the bed is at the top. Meanwhile, the patient's arms should be resting at their sides.
Application & Usage: It can be helpful for patients with hypotensive since it encourages venous return. However, it is used to offer posture drainage of the basal lung lobes.
This position can be in the prone or lateral position. The lateral knee-chest position has the patient lying on their side, the torso obliquely positioned on the table, and the knees and hips flexed. On the other hand, in the prone position, the client stoops on the table and lowers his shoulder on the table, so his face and chest rest on the table.
Application & Usage: Knee-Chest Position is used for sigmoidoscopy without anaesthesia. However, the position for patients can be weird.
Some other Patient Positions in Nursing:
Final Words
Designating a position is an integral part of nursing practice and is the responsibility of the Enrolled Nurse. Adequate positioning of patients provides proper ventilation and airway management, anatomical protection and maintains body alignment in most settings.
Related Topics: